脚手架架构设计和框架搭建
脚手架的作用
开发脚手架的核心目标是:提升前端研发效能
脚手架的核心价值
- 自动化:项目重复代码拷贝/git 操作/发布上线操作
- 标准化:项目创建/git flow/发布流程/回滚流程
- 数据化:研发过程系统化、数据化,使得研发过程可量化
和自动化构建工具的区别
- 不满足需求:jenkins、travis 通常在 git hooks 中触发,需要在服务端执行,无法覆盖研发人员本地的功能,如:创建项目自动挡化、本地 git 操作自动化等
- 定制负责:jenkins、travis 定制过程需要开发插件,其过程较为复杂,需要使用 java 语音,对前端开发不够友好
入门
脚手架本质上来说,是一个操作系统的客户端。
它通过命令行执行:
vue create vue-test-app
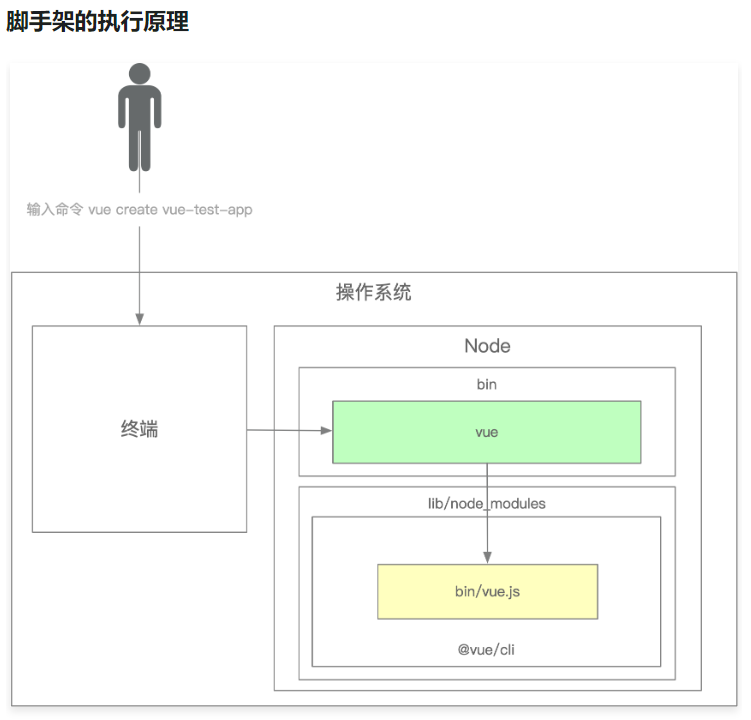
脚手架的实现原理
通过 npm 全局安装一个 脚手架例如 @vue/cli 后,会解析 package.json 文件中的 bin 配置
去在全局的bin目录下(/usr/local/bin),创建一个软连接,链接到全局的node_modules目录下
@vue对应的执行文件(../lib/node_modules/@vue/cli/bin/vue.js),
软连接的名称就是 bin 配置的 key,连接的文件就是 bin 配置的 value,value 指向的文件中需要设置 #! /usr/bin/env node
来标识文件需要用node来执行
基于 lerna 搭建自己的脚手架并且发布到 npm
安装方法
npm install -g @sunshine-cli/core
执行命令
sunshine-cli
进阶
理解 yargs 常用 API 和 开发流程
#!/usr/bin/env node
const yargs = require('yargs/yargs')
const dedent = require('dedent')
const log = require("npmlog")
const { hideBin } = require('yargs/helpers')
const pkg = require("../package.json");
const context = {
lernaVersion: pkg.version,
};
const argv = process.argv.slice(2)
const listCommand = {
command: 'list',
describe: 'list local packsges',
aliases: ["ls", "la", "ll"],
builder: yargs => {
return yargs
},
handler: argv => {
console.log(argv)
}
}
const cli = yargs()
yargs()
.usage("Usage: $0 <command> [options]")
// 配置脚手架的用法
.demandCommand(1, "A command is required. Pass --help to see all available commands and options.")
// 配置最少需要参数的个数
.recommendCommands()
// 当输入的命令不对时,会根据算法去匹配最接近的正确命令的提示
.strict()
// 无法识别的信息错误提示
.command(listCommand)
// 向脚手架注入命令
.options({
init: {
describe: 'init scaffold',
type: 'string',
alias: 'i'
}
})
.fail((msg, err) => {
// certain yargs validations throw strings :P
const actual = err || new Error(msg);
// ValidationErrors are already logged, as are package errors
if (actual.name !== "ValidationError" && !actual.pkg) {
// the recommendCommands() message is too terse
if (/Did you mean/.test(actual.message)) {
console.log(cli.parsed, 'argv')
log.error("lerna", `Unknown command `);
}
log.error("lerna", actual.message);
}
// exit non-zero so the CLI can be usefully chained
cli.exit(actual.code > 0 ? actual.code : 1, actual);
})
.group(['help', 'version'], "Global Options:")
.alias("h", "help")
.alias("v", "version")
.wrap(cli.terminalWidth()).epilogue(dedent`
When a command fails, all logs are written to lerna-debug.log in the current working directory.
For more information, find our manual at https://github.com/lerna/lerna
`)
.parse(argv, context)
理解 lerna 实现原理
- lerna 是基于git和npm的包管理工具
- 实现原理
- 通过import-local判断当前工程中是否存在lerna包,有的话优先调用当前目录下的
- 通过yargs生成脚手架,主要包括globalOptions的创建、command注入、参数解析等等;command最主要的两个回调是builder和handler方法 ,分别的作用是builder用于构架命令是可以执行的参数、改命令用法的例子等,handler用于实现该命令的功能,比较重要
- lerna在本地开发时可以配置本地依赖,而不需要
npm link的方式只需要在package.json中配置"@lerna/add": "file:../../commands/add", 即可,在代码发布时(lerna publish)会自动替换该路径
import-local 实现原理,理解 require.resolve 实现原理
- import-local主要作用是查找本地项目中是否存在该package,有的话会优先用本地的,这样的好处是可以解除全局和本地版本冲突的问题
- 实现原理
 重要实现
重要实现- fs.realPathSync该方法当找到路劲中存在软连接时,会重头开发在查找一遍,这样做的目的是为了防止软连接中还有软连接
- 遍历过程中生成的子路径会缓存到knownHard和cache中,这样的好处是提高查询效率;
- 遍历完成后得到的真实路径也会添加到缓存中,key为原始路径origin,下次就可以直接从缓存中拿到结果